1. Introduction
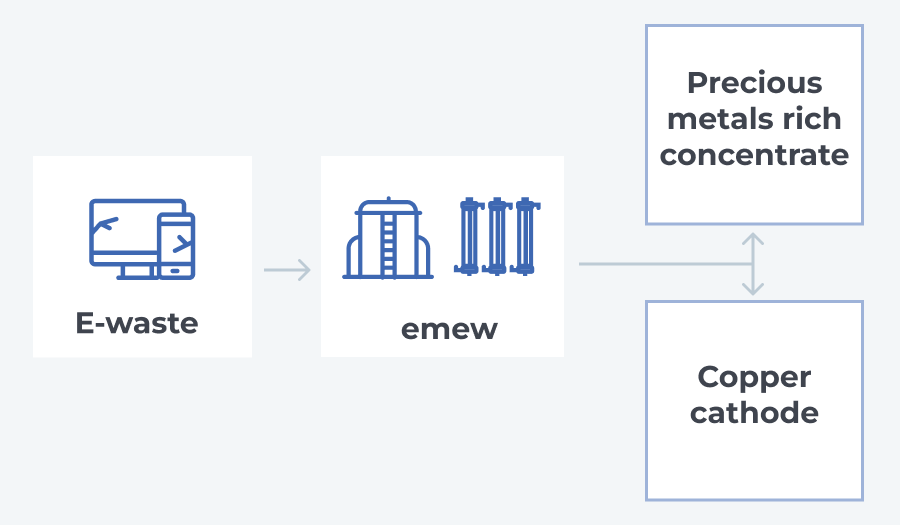
The discussions in earlier blog posts have delved into the value of metals in various types of electronic waste (E-Waste), the magnitude of E-Waste generation, and different processing methods. A search on these subjects reveals extensive articles and technical papers. Nevertheless, certain crucial aspects related to the operational and financial dimensions of managing an e-waste business are seldom explored and are frequently less comprehended by individuals not directly engaged in the operations of such enterprises. Operators typically refrain from openly discussing these matters due to their proprietary nature, contributing to their competitive advantage.