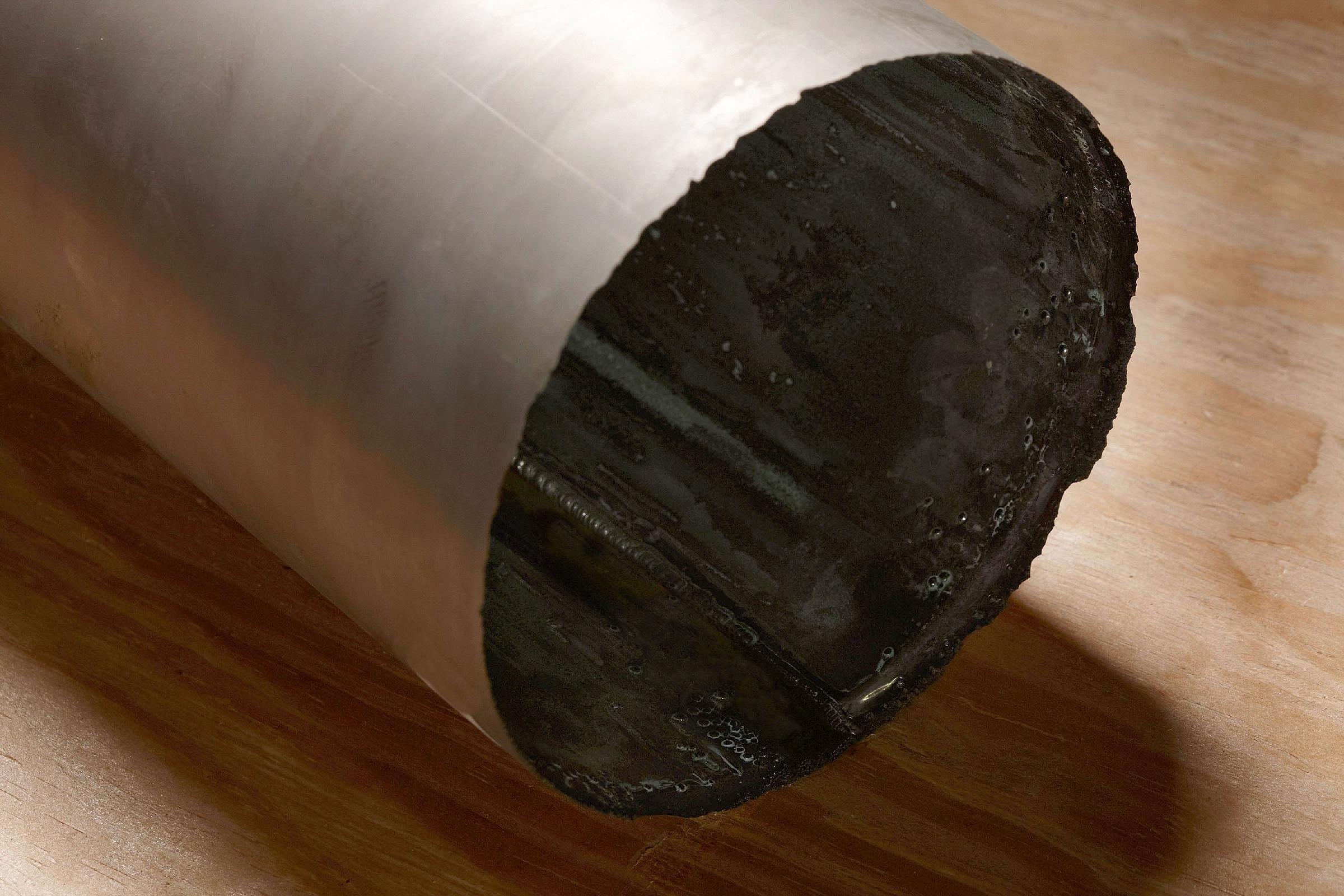
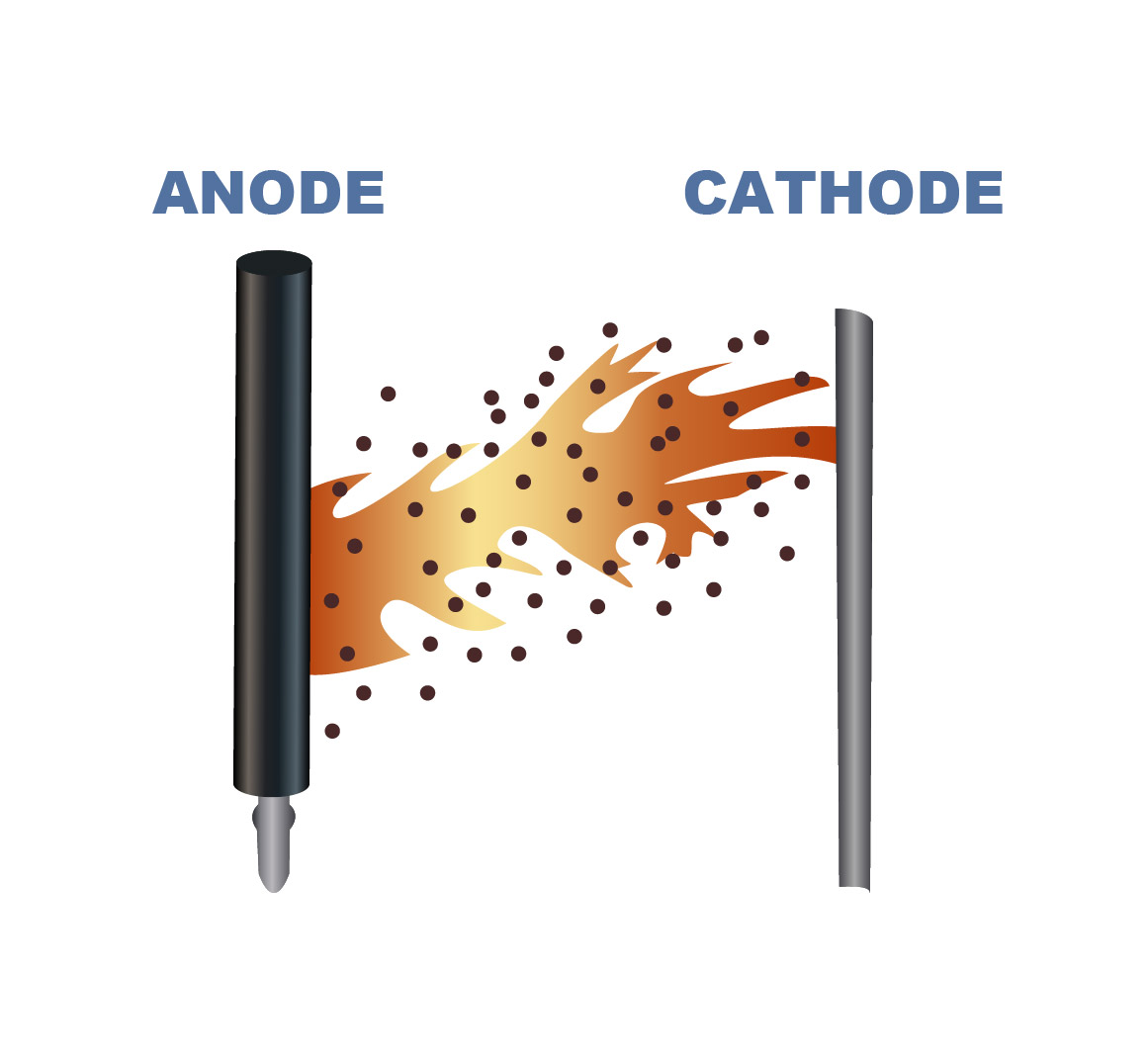
What are the Factors that Affect Anode Life?
In electrowinning, metals ions dissolved in an electrolyte are deposited in a reduced metallic form at the cathode. The conversion of the metal from an ionic (dissolved, positive charge) to metallic form (solid, no charge) at the cathode requires a supply of electrons into the electrolyte solution which is supplied from the anode.
Read More
Topics:
electrowinning,
anodes
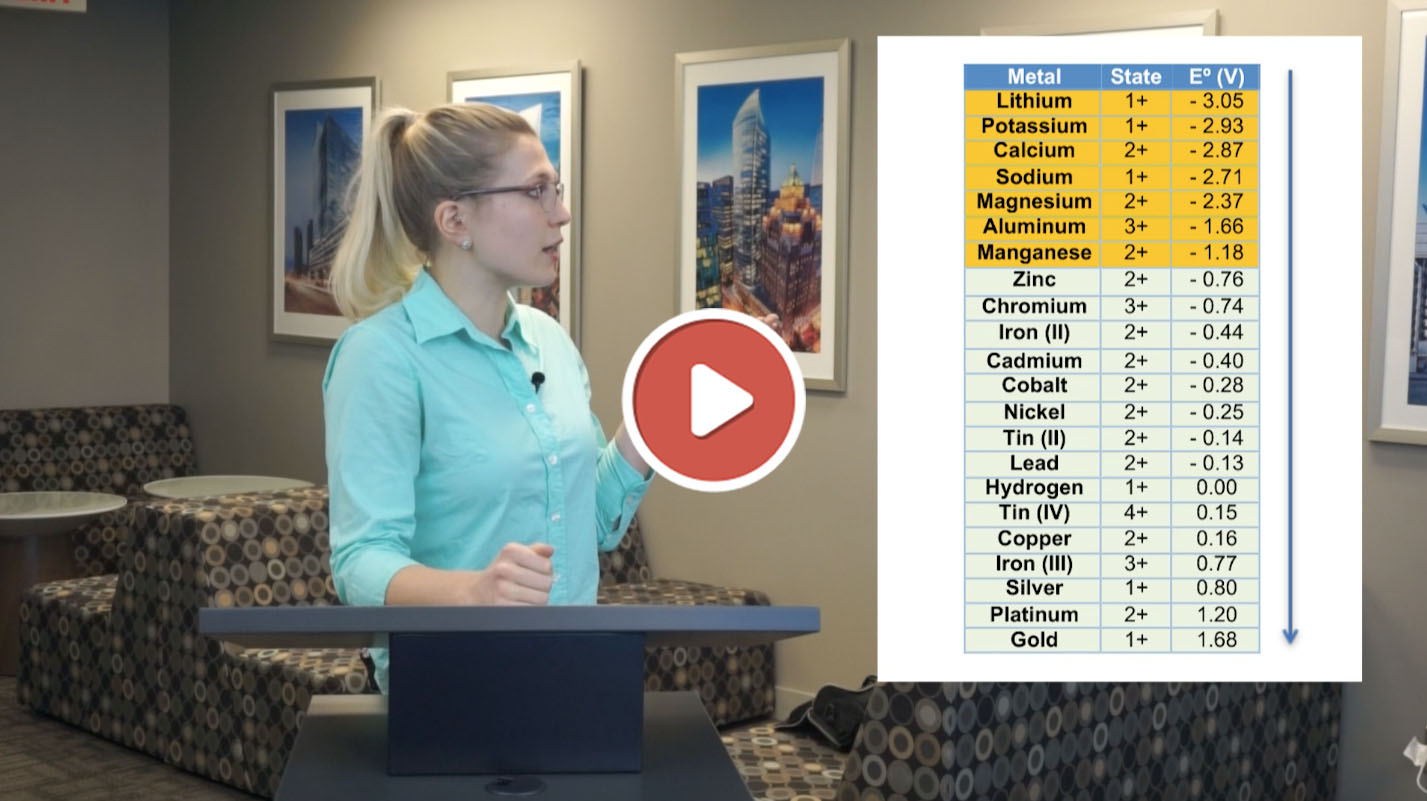
Why is it easy to electrowin some metals, and almost impossible to electrowin others?
In a few minutes, I will explain why. The answer lies in the Electrochemical Series, and its relation to electrowinning.
Read More
Topics:
electrowinning,
General
Due to the increase in electric and electronic equipment (EEEs), high-purity silver continues to be in high demand. For the past 4 years, silver demand has exceeded silver mining production, but the global supply has nearly met the demand each and every year – thanks to silver recovery and silver refining. Silver recycling will also be critical to meet future demand, especially as we see the general demand of metals increase across the globe, in relation
with
technological growth. High-purity silver can be produced from
silver refining and silver recycling by utilizing a series methods and processes, such as silver electrowinning and electrorefining. I’d like to delve into how these processes are carried out, and the outlook for silver production.
Read More
Topics:
metal recycling,
electrowinning,
emew,
Refining,
metal powders
1. What is electrowinning?
Electrowinning is a process in which metal ions present in an electrically conductive solution are separated using a direct current. This is achieved when a direct current is applied across an anode and cathode that are submerged in an electrically conductive solution causing the metal to deposit on the cathode. We say that metals like these were
electrowon.
Read More
Topics:
electrowinning,
Refinery Optimization
In a world that is increasingly demanding sustainability, nonferrous metal recycling has become a very important practice. Opting for recycling does not only mean being responsible for the environment and reducing the carbon footprint, it is also a very reasonable business in industries that rely on using non-renewable resources.
Read More
Topics:
Wastewater Treatment,
metal recycling,
electrowinning,
Refinery Optimization
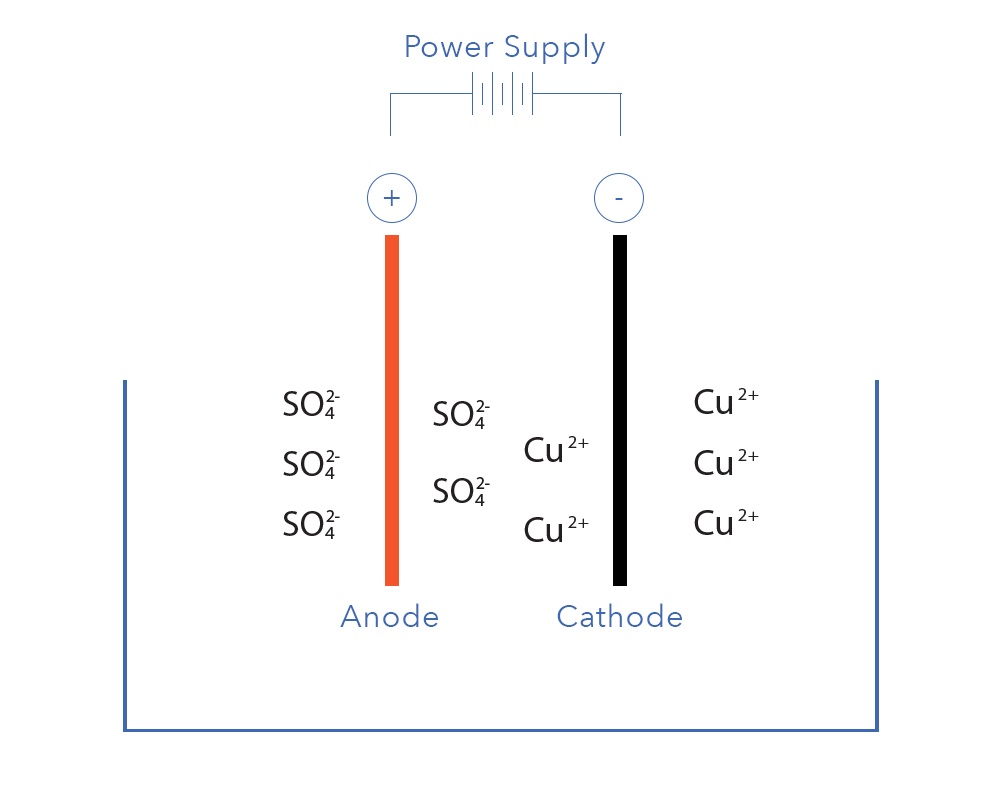
The electrowinning of copper is an electrolytic process that uses electricity to recover dissolved copper from solution as
copper
plate, also known as ‘cathode’.
Cu2+(aq) + 2e- -->Cu(s) (E0 = +0.34V)
Copper easily dissolves in acids including sulphuric, nitric and hydrochloric. Recovering copper cathode from acidic
sulphate
solutions using electrowinning is a well-known and fairly straightforward process that has been in commercial use since the late 19th century.
Read More
Topics:
copper,
electrowinning,
emew,
Refinery Optimization
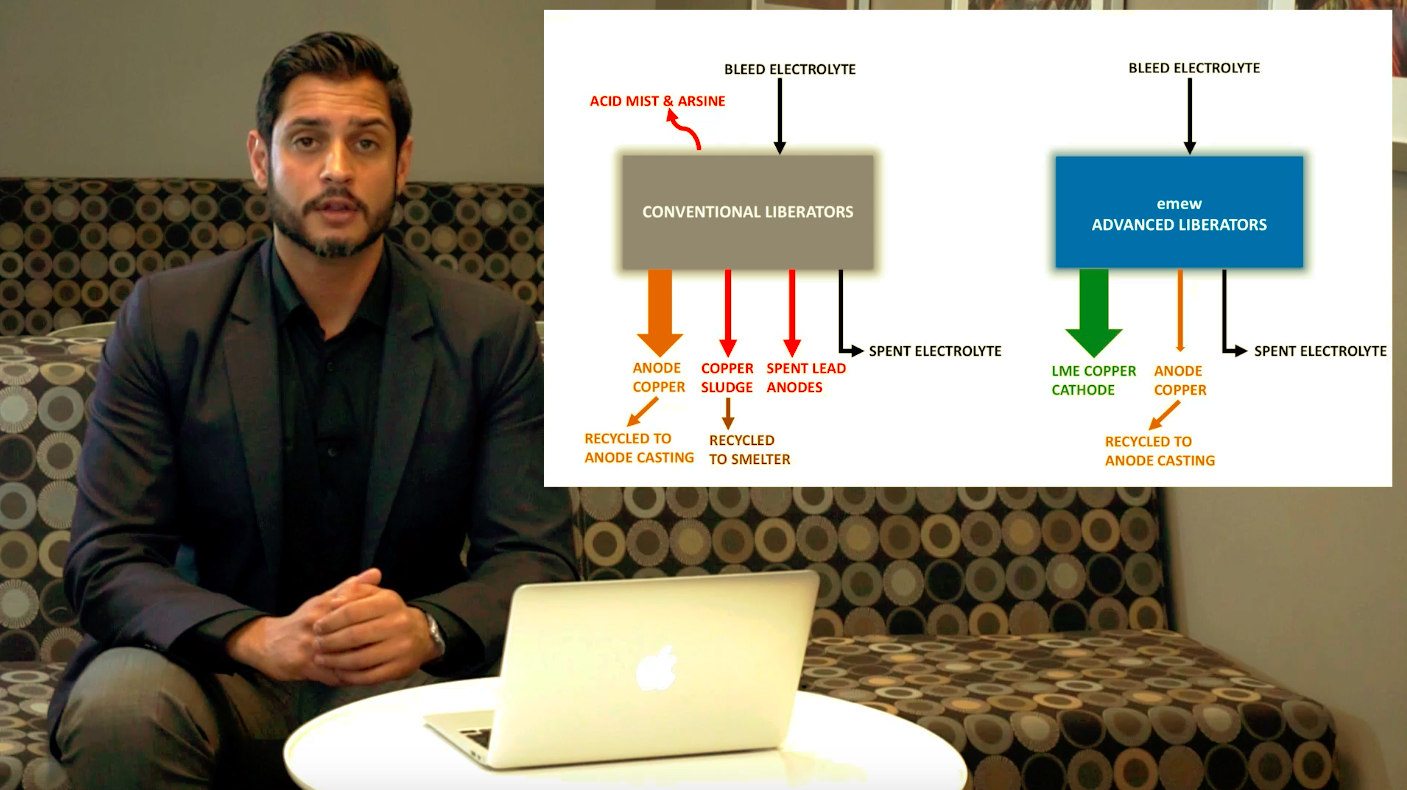
Thanks for joining me today for this discussion on emew advanced liberators. Let's start by looking at a simplified copper
refining process flow diagram. Copper Concentrate is fed to the smelting process where fire-refined copper is produced. Next onto anode casting, where 99% anode copper is formed followed by electrorefining of copper to produce LME grade copper cathode. But we aren’t done there, the refinery bleed is then sent to
copper liberators to control the copper concentration and impurities in the process. It is at this step, where we will focus our time today.
Read More
Topics:
electrowinning,
mining,
emew,
Refining,
Refinery Optimization
Electrowinning is known as an electrolytic process because it involves electrodes submerged into an electrolyte.An electrolyte is simply a conductive solution formed by dissolving positively and negatively charged ions.
Read More
Topics:
electrowinning,
emew,
Refinery Optimization
Electrowinning is the process of ‘winning’ dissolved metals from solution by passing an electrical current through an electrolyte containing said metal. The fundamentals of the electrowinning process have been discussed in a previous blog. The relative ease of recovery depends on the electrochemical potential of the target metal relative to the Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) which is defined by the following reaction:
Read More
Topics:
electrowinning,
nickel,
emew,
Refinery Optimization
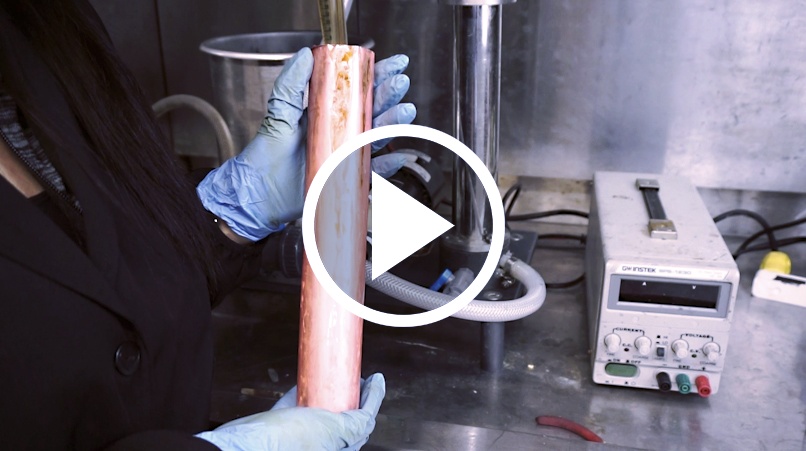
Lab tests such as this are an ideal way to demonstrate the recovery capabilities of emew for a variety of electrolytes and feed materials. In most cases, these tests can be done right at your site so you can see the results for yourself.
This particular test is to demonstrate the recovery of copper cathode from a copper sulphate feed solution. We can test a range of feed materials to recover not only copper, but also silver, nickel, tin and others. This copper sulphate solution was prepared ahead of time and roughly 3L transferred to the feed tank.
Read More
Topics:
copper,
electrowinning,
emew,
General